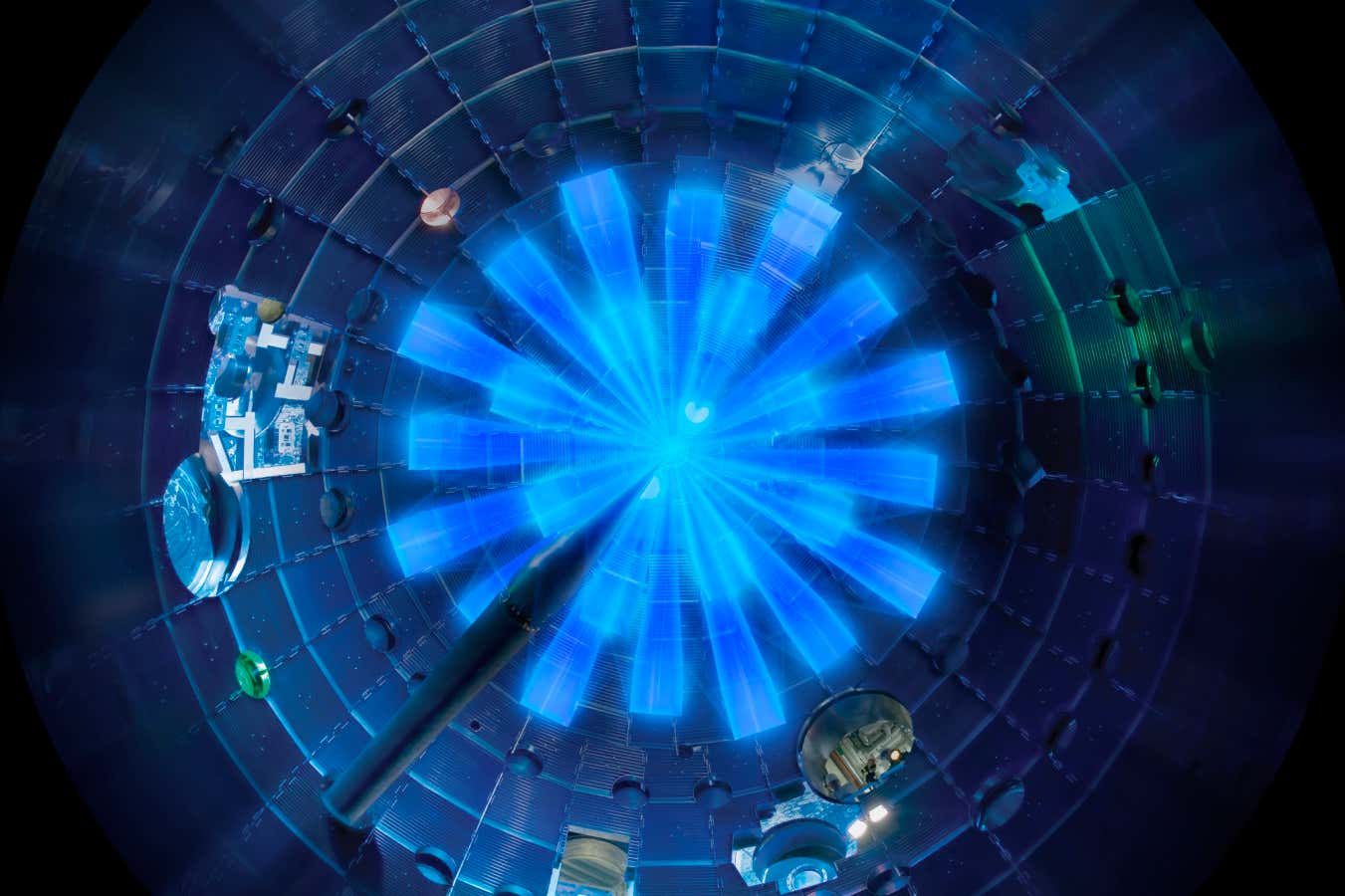
Excluding all the ancillary services, including the lasers that maintained the plasma, which was the principle part of this latest test.
Factoring everything in, they’re at about 15% return.
This is still very good for this stage, but the publications are grossly misleading.
I want to add that experimental reactors used for scientific research might never become net energy positive and that would be fine. Their purpose isn’t to generate profit, it’s to learn more about the physics, so it will be more valuable for them to be adaptable than efficient.
However, that doesn’t mean that you can’t take a configuration that has been shown to have potential and make a reactor that is more efficient than adaptable and use that to generate power for the electrical grid.
Basically, they have two different purposes.
Absolutely. Also, the fact that the reactor was only running for a short time plays a part. Usually there is a significant energy cost in starting and stopping, which is offset by running for a long time. However, these reactors are not designed for continued running.
It’s all a process of development, and even though the article is perhaps a little sensationalist, they’re making good progress.
but the publications are grossly misleading.
I think you’re only referencing the headline, the article itself clearly states what you said
Is the headline not part of an article?
When one says a publication is grossly misleading, it certainly implies the entire publication
Often the author doesn’t write he headline. Not sure it matters but most a bit of info.
You’re not wrong, but we also should stop excusing, normalizing, and accepting wildly exaggerated for sales purposes titles of articles.
We should stop accepting lies.
Unless there is some way this reaction actually did produce twice the energy input, it’s not misleading it’s a lie.
Why have we accepted the standard of misleading headlines? “Oh well you didn’t read the article, I guess you and 90% of eyeballs get to be fundamentally misinformed” is an unhinged take.
I never said a misleading headline was acceptable. I said the publication is not misleading and that it covers the criticisms dude up above was leveling.
It is misleading, for someone to be misleading they must mislead, and the headline misleads.
The headline is part of the publication though.
No, this is a popular science article, not an actual publication.
“article” vs “publication”
Two different things.
The link takes you to an article. Publications are in actual scientific journals, not intended for popular consumption.
What was your question? I only read “is the” and thought I could base my response off of only that.
When I see “publication” I assume it’s the actual scientific paper and not the article reporting on said paper.
That’s a great point. I absolutely agree with you on that.
It’s easier to nitpick than it is to interact with the actual argument.
I agree with you. The headline is misleading, and I think it devalues the article.
Generally no
Lol ok
The publications are not misleading, just these headlines.
That’s what I came to the comments to find. Thank you. Would have been much bigger news if it was net energy positive.
15% return is still net energy positive isn’t it? Or is that not 15% above the input?
I can’t read the full article (paywalled for me) but it references the National Ignition Facility so the way it goes is super lasers blast a tiny hydrogen thing and that creates a tiny bit of fusion that releases the energy. The energy of the laser blast is what’s being called the input and the fusion energy released the output. What is misleading is that a greater amount of energy was used create the laser blast than the laser blast itself outputs. If you consider the energy that went into creating the laser blast the input (rather than the laser blast itself), then it’s usually not a net positive energy release.
What other energy are you referring to? Like warming up the laser?
Remember when incandescent light bulbs were the norm? They worked by sending full line voltage through a tiny tungsten wire that would get so hot that it glows, making some light, but 95% of the energy that gets consumed is frittered away as heat? The high-power lasers needed to make fusion happen are a lot like that.
I believe all this article is saying is that 15% more energy than what came out of the lasers as useful laser light was liberated in the reaction.This completely ignores the energy it took to power those massively inefficient lasers.
I think it also ignores the fact that the 15% more energy liberated wasn’t actually, like, harnessed by a generator. I believe (and I may be wrong) this was testing only the reaction itself. Actually hooking that up to a turbine and using it to create energy that is cost competitive with contemporary sources is still a completely unsolved problem.
[email protected] got it, but basically lasers are pretty inefficient. The article I just found said (in a different run of this facility) they put 400MJ into the laser to get 2.5MJ out of it. So that makes the whole firing system what, 0.6% efficient? Your fusion reaction would have to give more than 400MJ to truly be in the positive for this particular setup/method, but again this facility is a research one and not meant to generate power - there isn’t even a way to harness/collect it here.
Oh so the laser’s generating mostly heat and a little coherent radiation, and they’re only referring to the coherent radiation as the “energy input” to the process.
Hmm. Kinda sketch.
Especially because that’s not trivial. If we have no way of obtaining laser light other than that process, and the laser is the only way to feed the fusion reactor, then that’s 100% on the balance books of this process.
Thx. Rip tho
From another article: “In an experiment on 5 December, the lab’s National Ignition Facility (NIF) fusion reactor generated a power output of 3.15 megajoules from a laser power output of 2.05 megajoules – a gain of around 150 per cent. However, this is far outweighed by the roughly 300 megajoules drawn from the electrical grid to power the lasers in the first place.”
That’s worded strangely (powering the lasers takes both 300 and 2.05 megajoules?) but oof
Powering the laser takes 300 MJ but the actual laser power (the energy in the light) is only 2.05 MJ. The rest of the energy is lost to heat and other inefficiencies. If the laser could be created with 100% efficiency then the input energy would also be 2.05 MJ.
Energy can be measured as occurring in different physical phenomena. There is energy in sound waves/packets, energy in light waves/packets, energy in matter, etc.
The 300 MJ number refers to the electrical energy in the form of electromagnetic fields carried specifically through solid conductors via electron movement along the conductors.
The 2.05 MJ number refers to the radiative energy in the form of electromagnetic fields sent specifically through free space/a vacuum (I presume; I didn’t read the article, so maybe the laser medium was a vacuum or something else) via photons/waves. No electrons, aside from those in the lasers that create the photons in the first place.
So there is a conversion from electric to radiative energy here.
Start Edit:
And as another commenter said, in this conversion there are losses because materials aren’t perfect.
:End Edit
If the 3 MJ radiant energy from the nuclear material was then converted back into electric energy via steam processes, we’d get a comparable number compared to the 300 one.
This is also why you see nuclear/CSP plants quoted in MWt and MWe: there is a conversion that takes place from thermal energy (vibrations of atoms/compounds) into electric energy.
If anything has been consistent about fusion its always them desperately trying to spin babysteps and monumental leaps forward and trying to make themselves seem super clean and safe especially compared to fission.
If anything has been consistent about fusion its always them desperately trying to spin babysteps and monumental leaps forward
That’s usually the media outlets sensationalising the results to the point where the articles are grossly misleading.
trying to make themselves seem super clean and safe especially compared to fission.
That’s just a fact, no need to try. The Fusion process is inherently safe the radioactive byproducts are generally short lived and easier to handle.
If publications keep misreporting your work, stop talking to them, and see different publications with a stronger commitment to the truth.
Fusion is not inherently safe. It has significantly higher rate of neutron discharge for the enegy produced which can damage the reactor vessel and potential to cause nonfuel material to become radioactive.
Ontop of any power disruption of the system has the potential for radioactive plasma to escape with nothing even remotely equivalent of a SCRAM to bring it back under control.
The only reason fusion appears safe right now is because its all still developmental phase and any issues are being handwaved as prototyping issues and not treated like the actual potential catastrophes they are.
The total mass of reactants in the fusion chamber is below milligram, some of which is bound in stable isotopes. Even if all of it escaped, it would be far from catastrophic.
The reaction itself cannot run away on its own because it requires a delicate balance in temperature and density, which will be immediately disturbed if there was a breach in containment.The walls will be activated by neutrons, but short of blowing the reactor up, there’s not much chance of materials escaping in a significant amount to pose a danger.
Just for comparison: The nuclear safety requirements of a fusion reactor are ballpark those of the radiology department in your local hospital: An accident will give you, if you’re unlucky, a dose on the order of a dental x-ray. Decommissioning involves letting it sit there for 100years until it has cooled down to ambient radioactivity levels, if you’re cheeky you could send it to a place where the natural radiation levels are higher and declare it cool much faster.
Why does noone talk about those ludicrously strong magnet fields and gigantic vacuum vessels? You’re standing right next to a massive volume of practically nothing and are worried that something leaks out?
Sigh, here we go, the propaganda is already starting lol
Fusion reactor SLAMS surprised scientists with it’s INCREDIBLE output
You’ll never believe what they do next!
What happens in the reaction at the 69th microsecond will shock you!
Fusion engine stuns EV industry!
With this weird little device you can do that at home I’m 90 seconds!
No, really, you can.
The end 😂😂😂
Scientists RIP stubborn atoms for bad faith energy negotiation policy.
Firstly, the energy output falls far short of what would be needed for a commercial reactor, barely creating enough to heat a bath. Worse than that, the ratio is calculated using the lasers’ output, but to create that 2.1 megajoules of energy, the lasers draw 500 trillion watts, which is more power than the output of the entire US national grid. So these experiments break even in a very narrow sense of the term.
It’s so refreshing to see an article at least mention the way these tests are measured are based on the energy just in the laser itself and not the total energy used.
I agree it’s good that the article is not hyping up the idea that the world will now definitely be saved by fusion and so we can all therefore go on consuming all the energy we want.
There are still some sloppy things about the article that disappoint me though…
-
They seem to be implying that 500 TW is obviously much larger than 2.1 MJ… but without knowing how long the 500 TW is required for, this comparison is meaningless.
-
They imply that using more power than available from the grid is infeasible, but it evidently isn’t as they’ve done it multiple times - presumably by charging up local energy storage and releasing it quickly. Scaling this up is obviously a challenge though.
-
The weird mix of metric prefixes (mega) and standard numbers (trillions) in a single sentence is a bit triggering - that might just be me though.
Electricity stuff is funny because it combines metric and imperial units sometimes to make bastard measurements
Huh? Whatchu talkin bout Willis?
Watt is a Joule per second
Volts, Amps, kWh, MJ… These are all metric.
Sssch don’t tell the Americans or they will try to wrangle in BTU in nuclear power plants
WE INVENTED IT AND BUH GAWD, WE WILL MEASURE IT IN MURICA UNITS!
Ignore how nonsensical BTUs are: Gonna shove energy and weight into a single measurement and it changes based on the initial temperature of the water.
Or HVAC uses tons of ice needed to cool something. Euroguys probably don’t have air conditioners, just that tilt window technology.
I do like the obscure AWG scale especially 0000
lol tilt windows
Y’all do know what BTU stands for, right?
British Thermal Units. It’s the energy needed to heat 1 lb of water 1 degree F.
The bad part is that no one bothered to set the starting temp of the water so there’s 5 separate standards for what the hell a BTU actually is, which makes it a really bad standard.
Yeah electricity is weird because Americans use metric for it. And it’s that way because metric predates it
Fun fact: While metric predates our full understanding of electricity, our understanding of electricity played a key role in the definition of the SI units.
As I understand it, the reason the SI unit for mass is kg not g - making it an outlier to my mind - is so that electical engineers could keep volts and amperes as convenient numbers.
Long read: https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.07306
In a number of instances where there is not a standard in place already it is not uncommon to see metric measurements mixed with imperial or US customary measurements.
I’m not in any way shape or form claiming that ALL of it is mixed.
However what does actually happen is the a unit of measure might be mixed with a customary one and then that becomes the defacto measurement, you may see wire resistance shown as a mix of Ohms/1000ft.
I am not getting into an argument about the merits of metric, I’m on board, I am with you. That doesn’t mean there aren’t some silly oddballs.
Is their an imperial equivalent to ohm?
It might be the case that imperial resistance is ohm the same as metric. Metric uses ohm as it’s constituent with base units of metric, but imperial doesn’t abide by rules like that.
If you had to make a imperial equivalent to resistance, it would be a fraction of the resistance of the monarchs finger.
Until we actually electrocute a king there probably won’t be
There’s no non metric electrical units except ohms/1000 ft or cross section dimensions, and AWG (and MCM kilo circular mils kcmils) versus mm^2
Why US uses awg with reverse scale instead of diameter is insane
formula: D(AWG) = 0.005·92^((36-AWG)/39) inch
-
Still, from an acorn grows a massive tree.
Exactly. These tests aren’t meant to create a practical solution, but to provide knowledge and insight that a) it is possible and b) exactly what is necessary to make it happen, at a physical level. Before this, it (more out than in) was all theory, but now we’re got some hard data to work with.
That’s a big step we’ve been chasing for a long, long time.
Yeah, and a good sign is that the countries with money to invest in the race all seem to be convinced we’ve got the science right and that the engineering challenges are solvable. There have been so many records broken recently we’re getting towards the end of the mile stones, hopefully soon we’ll start hearing about self sustaining experiments with records for how long they ran
That, is not an illusion, Master Oogway.
At some point we’ll be able to say: …and thus, humanity created its first star.
…and accidentally incinerated its home world, as the supply dependant lunar colony could only look on in horror.
✨The End✨
I know you’re joking, but nuclear fusion is inherently safe because if it breaks there is no way to sustain a chain reaction. And is only creates mildly radioactive byproducts. So you could blow it up and it wouldn’t seriously contaminate the area.
Not only are the radioactive byproducts not that dangerous (everything is relative of course). But also they have incredibly short half lives so they go away long before the firefighters turned up.
Technically fission has a similar physical barrier to infinite meltdown. Once the water leaves the core, the reaction stops. It was called China Syndrome, and we wouldn’t have worried about it at all, had the physicist that thought it up been a bit more competent with his math skills. Unfortunately, there are plenty of other ways that the reactors that we currently use can catastrophically fail.
Nah, the Earth doesn’t have enough mass to become a star. If it did, it would already be one.
I mean, no, it also doesn’t have enough hydrogen.
Everything’s hydrogen if split enough ¯\_(ツ)_/¯
But we’re talking fusion
When they do they should come up with some original quote.
“The power of the sun in the palm of my hand”, something like that.
Melts Your Mouth, Not Your Hand
At least they won’t be in danger of falling flat on the ground, halfway through their Big Words, due to muscle atrophy, the way every single other “first person on ______” is gonna have
“That’s one small trip and fall for a human, one giant faceplant for mankind.”
And directly started demanding money to use some of it.
We already got plenty of nuclear fusion output with no energy input on our part. But folks dont want solar panels
What is with peoples insistence that we only ever use one kind of power generation?
Wind, solar, fusion, fission, hydro, they all have their uses. Why limit yourself like some kind of console fanboy?
That’s fair. Im big solar fanboy but if more people were fusion researchers the world wouldnt be a worse place.
Fusion is self sustained and highly scalable.
If it was practical we wouldn’t need the other forms, except for places not serviced by electrical grids.
Fission takes a long time to build and finance. It hasn’t been invested enough in. We need more green energy to replace fossil fuels faster than governments can get fusion plants up. That’s why wind, solar and hydro are and should be the preference.
Hydro needs the right geography. Solar and wind need the right local weather. Solar great in a California desert, but terrible in Scotland where wind and hydro are very effective.
There some cases where a specific technology is the best and clearest option. But when fission becomes reliable, it will cover the vast majority of use cases in the highly Industrialised nations. Everything else will be niche.
Well as soon as I can get a fission reactor in my house I’ll give up on energy independence then.
Why limit yourself like some kind of console fanboy?
Propaganda by solar bros.
It’s only the solar bros doing this because you can sell solar to the average idiot. Most people can’t own other forms of clean energy generation directly.
I also have a suspicion that a lot of the renewables vs nuclear debate is stoked by fossil fuel interests
*minus the energy needed to make, maintain, and replace solar panels.
I support more solar installations, just calling out it isn’t free power.
As more solar is installed, the less power input we need to provide. There will be a point where all solar power required to make a solar panel will be produced by solar panels
As more solar panels are installed, more material and maintenance are required. They deteriorate over time, and require large physical areas.
I guess at that point, each panel needs to be extremely efficient to limit the space, extremely durable, made of cheap materials, easily recyclable into another panel.
Right so
No energy input on our part
Is clearly false
I give the comment a pass because it’s pretty obvious hyperbole
True, but that’s not reliable source of energy though, specially during short and cloudy winter days when it’s most needed. Look what happened in Germany and how they became on if the biggest European polluters. The key ingredient missing is energy storage. Once that’s solved, solar panels would become much more useful.
We could massively subsidize home battery storage and this wouldn’t be an issue at all. Microgrids are the future anyway. The only reason why storage is an issue now is because it needs to be centralized. Once we get away from that tons of new possibilities open up.
Home batteries are expensive and take a lot of place. Also they won’t last more than a day. Imagine winter time with short cloudy days. Realistically you need at least a month worth of energy storage and even then you need sun to recharge it. They would distribute energy consumption better though by charging during night.
We have all the technology for energy storage we need, it just needs to be built. Theres gravity storage like pumped hydro, pressure storage, thermal storage, flywheels.
Well, no. Sadly we don’t. At least not in the range needed. All of these require either specific geographic relief, something really huge, too expensive or combination. Perhaps the most promising is the green hydrogen, but then again, we have yet to see it at such scale. I’d love to be wrong, though.
something really huge
yeah, we use a lot of energy, absolutely every form of energy production we have involves really huge things. Massive mines, dams, pipelines, oil rigs, nuclear cooling towers, fossil fuel power plants, oil tankers. They just have to be built. we can excavate dams, build solid weight lifting facilities, molten salt storage, make arrays of flywheels. There’s a ton of answers to energy storage already, they dont involve resources with any kind of scarcity, they just have to be built.
Big construction involves environmental concerns, that’s why we don’t have many new dams nowadays
Boi i better see you raising a fuss over that infrastructure bill
Grrl I don’t remember voicing my own opinion on anything
Or bombs. They have fusion versions of those with a great deal more output than input but they’re not really fond of those either.
Solartards don’t realise that the problem with solar is storage and sun availability. It’s a fantastic idea on paper but unless you’re in an tropical country, good luck surviving winters.
WHAT? This is completely new information that nobody has filled journals with papers working out solutions.
we’ve had grid scale storage for a long time now. storing energy for things like cars needed new technology for weight concerns, but for electrical utilities? You lift a weight upwards with an electric motor during peak times, and let the weight down to spin a generator when you need it. It’s been in application with pumped hydro storage for a while.
There are plausible technical designs to make huge batteries out of dirt / dirt cheap materials (e.g. liquid metal battery but there are others). I wonder how that compares to building other power plants. The problem is that humanity is just too stupid to live.
Yes, as evidenced by humans not living
Humanity as a global civilization, not individual humans. The latter you can have intelligent conversations with, the former has the rationality of a slime mold - only growing towards where there is energy / food / money.
Maybe one day we will produce a civilization capable of using technology as it comes out instead of one that decided to call it quits decades ago. Oh sure we got cellphones but we are still burning coal. Because nuclear is scary.
I think nuclear energy is a great idea in theory, but I have absolutely zero trust in companies handling nuclear waste responsibly. It’s not like they have a great track record.
That being said, pretty excited about this if it’s as safe as they say.
Because nuclear is scary.
Nuclear isn’t scary. It’s waste, on the other hand, is.
But you know, it’s not like we’ve not had multiple examples of nuclear power plants failing catastrophically and destroying things around them for miles, and for decades/centuries.
Having said that, if they did come out with new technology version of a nuclear power plant that is safe and that with a catastrophic failure does not harm the environment around itself then I would be all for it. I just don’t think the technology is there for that. I hear they’re working on it though.
In other words you want special pleading. All other energy techs are allowed to have problems and produce waste except for one.
I love Kyle Hill/subbed. It’s fair to say though that he’s very pro-nuclear. Not discrediting what he says, just saying he definitely has a certain perspective on it.
And my primary criticism is on the catastrophic failure problem, and while I think the storage problem is a negative as well, I think it’s less so than the catastrophic problem.
And my primary criticism is on the catastrophic failure problem
That’s the weaker argument in your original post. Modern designs are nowhere near as bad as older ones designs (aka soviet, we all know you mean Chernobyl) and even the older non soviet ones aren’t bad at all
Fukushima is nowhere near Chernobyl levels of damage (didn’t destroy things for miles for centuries), and no other major plant failures that I can think of would match “catastrophic failure”
That’s the weaker argument in your original post.
Well I mentioned waste first as I did that as a tongue-in-cheek response, but then I immediately mentioned in the very same comment the catastrophic issue, and my recent comment is just me elaborating on the fact that I gave one more weight than the other. It doesn’t discredit what I’m saying.
Fukushima is nowhere near Chernobyl levels of damage (didn’t destroy things for miles for centuries), and no other major plant failures that I can think of would match “catastrophic failure”
Fukushima exclusion zone is not large enough for you to consider that a catastrophic wide area failure? Really?
Modern designs are nowhere near as bad as older ones designs
I’m already commented on this, but just to quickly repeat myself, there’s a difference between being on the design board and being in existence in production.
Nuclear fusion does make this prospect potentially real. The only thing they emit is neutron radiation, and a mean lifetime of free neutron is 14 minutes 47 seconds.
As per current fission technology, while nuclear waste is real issue, nuclear power is historically one of the most ecological ways to produce power. Catastrophes are now less and less likely, with many lessons learned from Chernobyl and Fukushima - lessons that are now implemented in all reactors around the world.
I live in a city powered by a reactor of the same model there was in Chernobyl, but modified following the incident. I fully trust it.
Catastrophes are now less and less likely, with many lessons learned from Chernobyl and Fukushima
I swear I do not mean this as a disrespect on you, as your comment was well written/said, but I’ve been hearing that kind of phrasing from companies that run power plants that catastrophically fail for many decades now. I’m definitely in a once-bitten twice shy mode at this point.
I’ll leave it at this, I hope you’re right, but I can believe you, or my lying eyes (to quote a comedically philosophical man).
I live in a city powered by a reactor of the same model there was in Chernobyl, but modified following the incident.
I live nearby a nuclear plant (not Chernobyl design) as well, though now all three of its reactors has been decommissioned because of age.
I fully trust it.
You’re not trusting that Chernobyl style design (that’s flawed) you’re trusting it’s operators do not f up and trigger the flaw like they did last time with Chernobyl, and humans are never 100% perfect 24/7. Also, Mother Nature tends to have some input as well.
There already is tech that’s safer and tech for reprocessing the waste. The fact that we haven’t used it speaks volumes. It’s not profitable and never will be. So unless we move energy production back to government owned, it’s not going to happen. So yeah if it’s nuclear waste that lasts millions or billions of years vs spending some money on battery tech to compliment renewables until we get something like fusion tech, yeah, it makes no sense to invest in dirty energy.
Funnily enough, coal plants waste is infinitely more harmful than nuclear waste because the general public doesn’t see it as scary, so it’s barely regulated.
If companies can’t be trusted to dispose of coal waste properly, what’s the likelihood they’ll dispose of nuclear waste properly? And reactors that don’t produce dangerous waste, don’t produce enough energy to be worth the cost unless you add the cost of proper disposal of the waste. And since they don’t have to do that, they just store it in temporary storage pools indefinitely, the cost is much cheaper to stick with current tech. So fission will never be safe.
I don’t think companies can do that actually. It is very regulated area. Also I think there is a lot of nuclear scare going on. Nuclear is not at all dangerous as it most people think, it just sounds scary.
At present we have oil and coal companies that are responsible for a lot of deaths and burning the planet. Nuclear is in no way near ammount of damage coal and oil are making right now. So even with nuclear accidents(sounds scary yea) it’s better than coal and oil.
If you think companies care, you haven’t been paying attention. Nuclear waste will continue to pile up and will exist until the Earth is gone. You think we’ll store it safely that long? Keep replacing the containers. Protect it from natural disasters or wars. There is not safe place to put it that won’t eventually end up in the ground water and eventually evaporate and become airborne except deep inside the earth and we don’t have the tech and even if we did it would be way more expensive than just investing in new battery tech and renewables.
I don’t think companies care, I said > I don’t think companies can do that actually. It is very regulated area.
What I’m arguing for in favor of nuclear power sources is that is cleanest source of energy we have from all and least deadly from all. But the reasons we can’t have it on the entire world scale are in short, capitalism. Politics + oil/coal lobby.
It is oddly enough easier to store nuclear waste since it is very easy to contain. Coal waste is nearly impossible to do that. No matter how hot you burn or how much you scrub or what tricks you play with syngas/distillate you are still going to end up with CO2 in air.
But nuclear waste will be dangerous longer than any container could possibly survive. Plutonium 239 has a halflife of 24,000 years. Some uranium isotopes are as much as 4.5 billion years. And that’s half-life, not how long it will take to be not dangerous. That’s one reason Yucca Mountain was never completed and the US has zero permanent storage facilities. Eventually it WILL get into the ground water and it will be extremely difficult to clean up, if not impossible, before it contaminates a large area and possibly becomes airborne with evaporation. One earthquake, one change in the water tables that puts water in direct contact with the outside of the pools. One flood. One bomb. Maybe not in our lifetime, but it is inevitable. And if we end up with more power plants and acres and acres of temporary storage pools that will never find a place to put it, it’s going to be really bad. We can’t even get enough money to remove lead pipes or asbestos from most homes. How will we store something that will be dangerous until the sun goes nova.
I’m not saying to stick with coal. I’m saying why invest in using a dangerous energy source when renewables are plentiful? We just need better batteries to store the energy and release it more evenly.
Awesome put a solar farm next to a nuclear fusion plant
I believe the general principal is giving such a device “seed energy” to get it started, then just feeding the power it produces back into itself. The only time you’d ever need that solar farm is to get it started.
You could also pump that energy into other fusion reactors to get “unlimited energy” so to speak.
deleted by creator
Why would we want to get rid of fusion reactors? We literally have zero, and are working toward them being viable for general use.
I deleted the comment 3 seconds after it was posted, funny thing that you are still seeing it
8h later, I’m still seeing it too. Looks like the delete may not have either taken or may not have synced.
Deleted for me so probably an instance thing
Maybe I should start building the habit of checking what I wrote before I post instead of after
That’s not how nuclear power works
We’ll probably be able to harvest solar power from space then beam it to Earth in a practical way first, than nuclear fusion becomes practical.
There is a very efficient way to beam solar power from space. It is called light.
It’s not efficient, a huge amount of it gets diffused or absorbed
It doesn’t need to be efficient. Capture all the light that hits earth for 5 minutes and that’s the world energy demand for a year.
How would you store it though?
solar george
Solar Robert
Stéphane Robert
Usually In plants and algae.
Black hole
It’s not efficient, a huge amount of it gets diffused or absorbed
The amount that’s left over though is more than enough, especially with today panels which only convert a very small percentage of that remaining energy.
As the panels improve even more they’ll be a very large energy surplus, even with how much solar light actually gets through the atmosphere.
Wow, you’re right! We should just build a Dyson sphere around the sun. 100% efficiency achieved. What could possibly go wrong?
Did you understand the person you respond to as saying its inefficient because the sun shines in other directions than the array proposed?
I’m pretty sure the person talked specifically about the beam from the array to earth being inefficient.I was joking, but apparently nobody picked up on my snarky sarcasm. Disregard.
Where did I say that?
The nice thing about space is that there isn’t any weather up there to make the solar panels dirty etc. There’s also a lot of space, which solar panels need a lot of.
How would you move the power down to earth?
Microwave transmission is what’s usually said, then someone says anything in the beam’s path will get zapped, then it’s pointed out the energy density isn’t that high. Just wanted to shortcut that for ya
But what if I want to zap anything in the beam’s path?
Then a meddlesome British agent will interfere.
Well at least I still have my cat.
And my moon laser
Long cable
We need to make sure we knot it at the joins so it doesn’t get accidentally disconnected.
Or just charge up car batteries and drop them.
Isn’t there already a tesla up there?
Checkmate, Elon haters
How would you move the power down to earth?
Last time I read up on it it was via converting the energy into microwaves and beaming it down.
I think masers (microwave lasers) are the new theory for achieving this, previously it was beaming microwave down much like your microwave oven beams your food.
It’s not that new. Sim City 2000 included a power plant that was just a receiving dish for a maser
Funny thing is, no matter how you arrange to do that it becomes a de-facto death ray. Stick a terawatt of solar panels in space, use the power to shine a laser/maser down to earth, then build a station to turn the laser power back to electricity? Great, until some hacker figures out how to control where the laser is pointed. Then you get Dr. Evil holding the world for ransom.
Nah it’s not really bad at all:
The use of microwave transmission of power has been the most controversial issue in considering any SPS design. At the Earth’s surface, a suggested microwave beam would have a maximum intensity at its center, of 23 mW/cm2 (less than 1/4 the solar irradiation constant), and an intensity of less than 1 mW/cm2 outside the rectenna fenceline (the receiver’s perimeter). These compare with current United States Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA) workplace exposure limits for microwaves, which are 10 mW/cm2,[original research?] - the limit itself being expressed in voluntary terms and ruled unenforceable for Federal OSHA enforcement purposes.[citation needed] A beam of this intensity is therefore at its center, of a similar magnitude to current safe workplace levels, even for long term or indefinite exposure.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Space-based_solar_power?wprov=sfla1
Lasers
The nice thing about space is that there isn’t any weather up there to make the solar panels dirty etc.
There’s a lot of junk though can that can damage those panels.
Space Lane cleaner was going to become a thing at some point anyway…
Not at the legrange point! Yet, anyway
Not at the legrange point! Yet, anyway
Actually, that’s not true. The latest telescope we sent up there has been getting damaged from the junk at that point.
And we can position a bunch over the poles to help stave off climate change.
The poles aren’t really the place that need that the most.
You wouldn’t think so but them staying super cold helps stabilize a large chunk of our climate. Also throwing shade on arable land isn’t great for food production.
They’re already really reflective and don’t get much light.
They’re losing reflectiveness as they lose ice and it’s one of the major drivers of climate change.
We dont need to collect it in space, just direct more of it to certain ground based collectors?
Increasing solar incidence will increase the planet’s temperature.
So will any other space collection of power.
what if we burn the co2 away
We might be able to burn this atmosphere away yet!
no stop
I’m not sure what comment to reply to, but I feel obligated to remind people that the sun is a fusion reaction.
solar powergravity confinement fusion
What?
Basically, the idea is to build orbital solar farms (where is always sunny), then beam the energy produced back to the ground with microwave transmitters and ground recievers. It’s technically feasible, unlike fusion we have all the technology needed to do it right now. However, it’s cost and resource prohibitive. The US government studied building such a system in the 1970-80’s after the energy crisis. We could do it, but building it would take a generation to get running and about double the US’s current military annual budget. Launch costs are coming down since then, but the industrialization of space and the moon will take generations and would need to be an international effort to have any chance of success.
You know, for a bunch of people who crave power, politicians sure don’t seem too keen on harnessing it.
Wait… Beam solar energy from space? That’s what the sun does?
We’ll probably be able to harvest solar power from space then beam it to Earth in a practical way first, than nuclear fusion becomes practical.
You mean solar panels?
deleted by creator
There was something about access to scientific articles being less accessible than ever before…and it was paywalled.
here you go - you can archive.is to bypass paywalls
nice to see more progress.
we need this now more than ever.
I thought because of the law of conservation of energy you couldn’t get more energy out of something you put in.
I’m getting troll vibes, but I’ll bite lol. Fusion reactions are the exception since you’re turning some mass into energy according to:
E = mc^2
There’s many quality videos on YouTube that can provide a better explanation than I ever could.
They’re not an exception to conservation of energy, it’s just that matter is energy in another form. Fusion reactors just harness that energy.
True, thanks for the clarification!
No worries 👍
You can think of the material being fused as fuel. More energy is produced by burning the fuel than in the spark it took to ignite it.
That doesn’t include the change in mass tho
Why are so many people talking about nuclear fission waste here?
I hope it is not too late for the dawn of this new technology
If there was a working lab design with constant, net positive output announced tomorrow, then it would take ten years before we saw a commercialized version.
Still worth pursuing, but it’s not going to be our savior.
To need a savior we would need saving.
If you look at the UN predictions on climate change it’s gonna alter like 2% of our world, slowing us down slightly. It’s not going to kill us.
What do you mean? Too late for you to get a job working on it?
Is it scalable?
It’s the NIF. It’s a hydrogen bomb simulator, it’s not intended to become a power production mechanism. Roughly 0% of their budget involves researching how to turn single fusion explosions at most every few hours into continuous power output.
Scales great for getting around nuclear test ban treaties though, much quicker to retest than blowing up Pacific islands.
That sounds like we just gave a bunch of nerds a videogame where they get to throw nukes at random scenery and then claim they’re doing science by writing down the results.